
Warm Edge
Spacer Bar
Warm Edge
Until recently, aluminium spacer bars were commonly used in the construction of IGUs. However, aluminium is highly conductive and results in significant thermal energy loss.
Insulated glass units
with warm edge
With the continuous improvement of window frames and glazing systems, along with a growing emphasis on thermal efficiency, the market has seen a major shift toward warm edge technology.
As reducing energy consumption becomes increasingly important, this shift has led to a demand for windows with lower thermal transmittance values (Uw [W/m²K]). The adoption of warm edge technology in insulating glass units has been crucial in meeting these energy efficiency goals.
Warm edge objectives
Warm edge products play a crucial role in minimizing energy loss. By significantly reducing the temperature differential between the centre and edges of the unit, warm edge spacer bars can cut heat loss (or heat gain) by up to 94% at the external edge of the window.

Reduce heat loss
with warm edge
technology spacer bar
Double-glazed windows with warm edge spacer bars feature a warmer internal edge temperature, improving thermal efficiency by up to 65%. This helps reduce the risk of condensation.
Warm edge technology can lower condensation on sealed units by up to 70%, significantly reducing moisture and nearly eliminating the chance of mold growth and harmful bacteria.
By enhancing heat retention, warm edge technology also helps reduce a home's heating or air conditioning needs, lowering carbon emissions and saving money on fuel bills.
Benefits
of moisture penetration
Specifications
Various spacer bars have been used within insulated glass units. Some were more thermally efficient than aluminium spacer bars, however, did not meet the industry criteria. With a major enhancement in the design standards, the below parameters were set in which the spacer bar had to fulfil to be classified as warm edge.
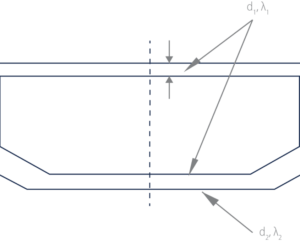
Σ (diλi) ≤ 0,007 W/K
where:
di – thickness of partition material
λi – television of conductivity of material in W/mK
Example: 2(d1λ1) + (d2λ2) ≤ 0,007 W/K
The table below shows how particular types of bars fulfil the revised criteria.
| Types of bars | Value ∑ (di x λi) EN ISO 10077-1 | Qualification assessment of spacer bar as “warm edge” |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminium | 0,1120 | negative |
| Stainless steel Chromatech | 0,0052 | positive |
| Chromatech Ultra | 0,0026 | positive |
| Termo TGI | 0,0020 | positive |
| Swisspacer Advance | 0,0019 | positive |
| Swisspacer Ultimate | 0,00002 | positive |
| Multitech G | 0,00002 | positive |
| Type of spacer bar | Colour | Widths |
|---|---|---|
| Thermobar | RAL grey 7045 black 9005 white 9016 | 10,12,14,16,18,20 |
| Swisspacer Ultimate | RAL light grey 7035 black 9005 | 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 |
| Multitech G | light grey black | 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 |